Enhancing Place Recognition using Joint Intensity - Depth Analysis and Synthetic Data
Abstract
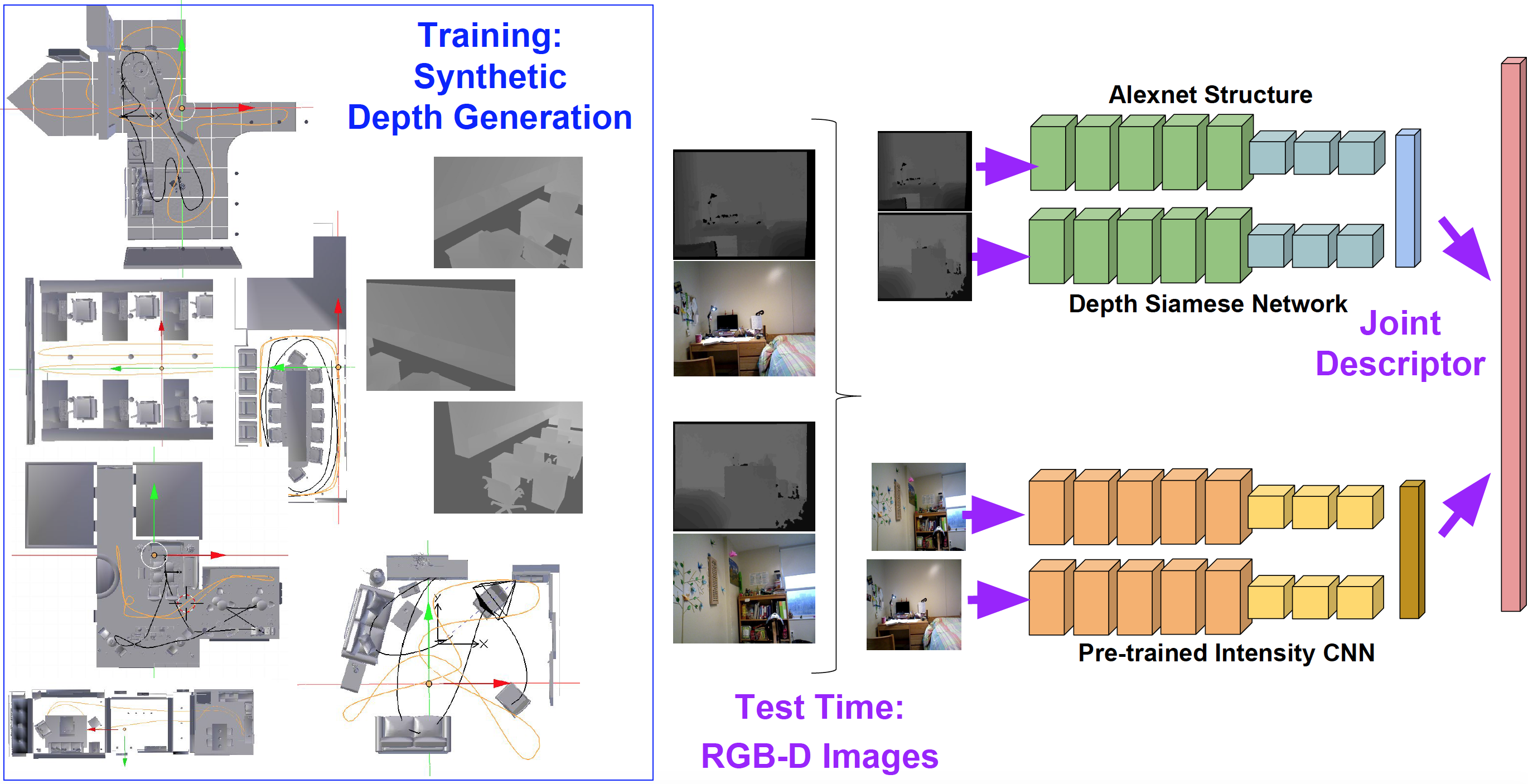
Visual place recognition is an important tool for robots to localize themselves in their surroundings by matching previously seen images. Recent methods based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) are capable of successfully addressing the place recognition task in RGBD images. However, these methods require many aligned and annotated intensity and depth images to train joint detectors. We propose a new approach by augmenting the place recognition process with individual separate intensity and depth networks trained on synthetic data. As a result, the new approach requires only a handful of aligned RGB-D frames to achieve a competitive place recognition performance. To our knowledge, this is the rst CNN approach that integrates intensity and depth into a joint robust matching framework for place recognition and that evaluates utility of prediction from each modality.
